MSE News and Events
Institute News
People with type 2 diabetes who contract COVID-19 are nearly 50% more likely to wind up in intensive care if they have poorly managed their blood sugar levels over the long-term than those with better long-term glycemic control, according to a study using anonymized health care data.
Researchers have developed a new technique for revealing defects in nanostructured vanadium oxide, a widely used transition metal with many potential applications including electrochemical anodes, optical applications, and supercapacitors.
A number of vulnerabilities, known collectively as deep learning adversaries, hold artificial intelligence (AI) back from its full potential in applications like improving medical imaging quality and computer-aided diagnosis.
Accurate predictive simulations of the electrochemical reactions that power solar fuel generators, fuel cells, and batteries could advance these technologies through improved material design, and by preventing detrimental electrochemical processes, such as corrosion. However, electrochemical reactions are so complex that current computational tools can only model a fraction of all relevant factors at one time — with limited accuracy. This leaves researchers reliant on the trial and error of significant and expensive experimentation.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, restaurants throughout New York City and elsewhere use bespoke outdoor structures to offer safer dining experiences for their customers. However, many of these installations do not adequately protect servers, physically separate diners, provide thermal comfort, or easily disassemble if street maintenance is needed.
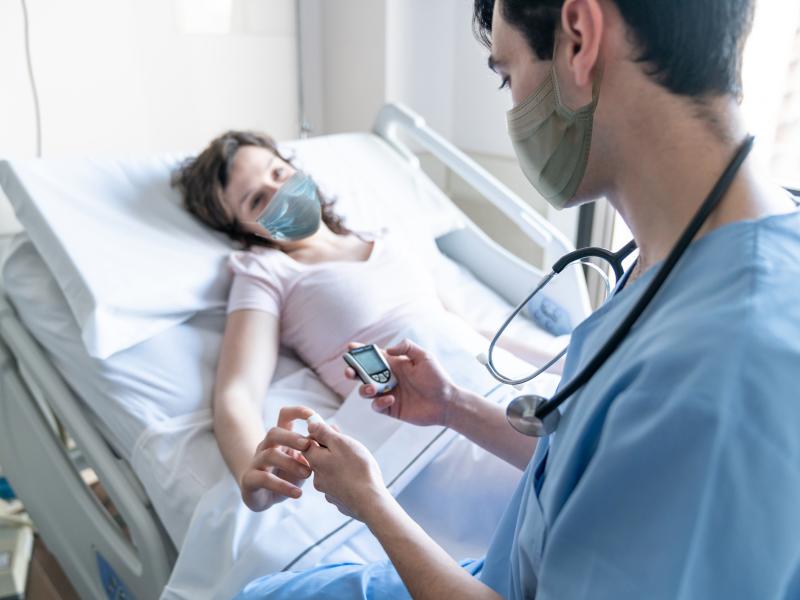

 Long-term Blood Sugar History Predicts Risk of Severe COVID-19 Among Diabetics
Long-term Blood Sugar History Predicts Risk of Severe COVID-19 Among Diabetics
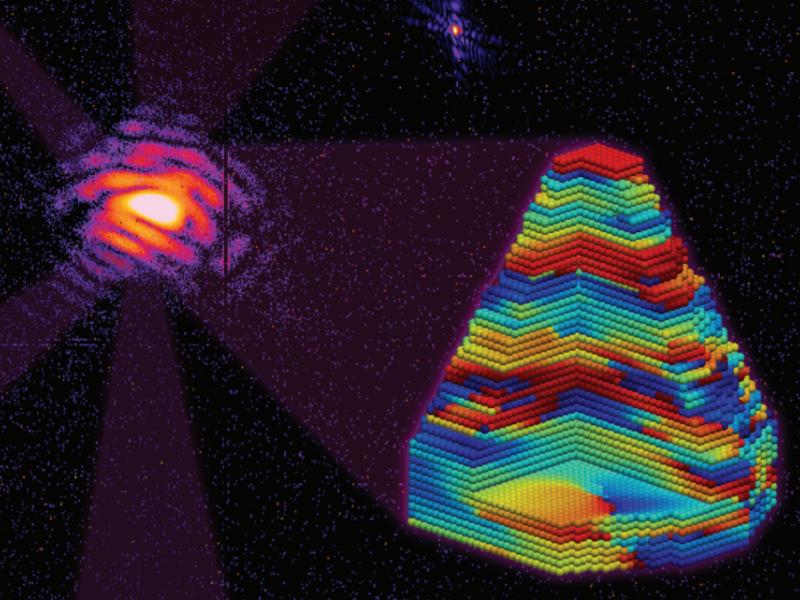 Imaging Technique Reveals Strains and Defects in Vanadium Oxide
Imaging Technique Reveals Strains and Defects in Vanadium Oxide
 Rensselaer Team Aims To Pave Way for Robust AI in Medical Imaging
Rensselaer Team Aims To Pave Way for Robust AI in Medical Imaging
 Advancing Future Energy Technologies With More Accurate Electrochemical Simulations
Advancing Future Energy Technologies With More Accurate Electrochemical Simulations
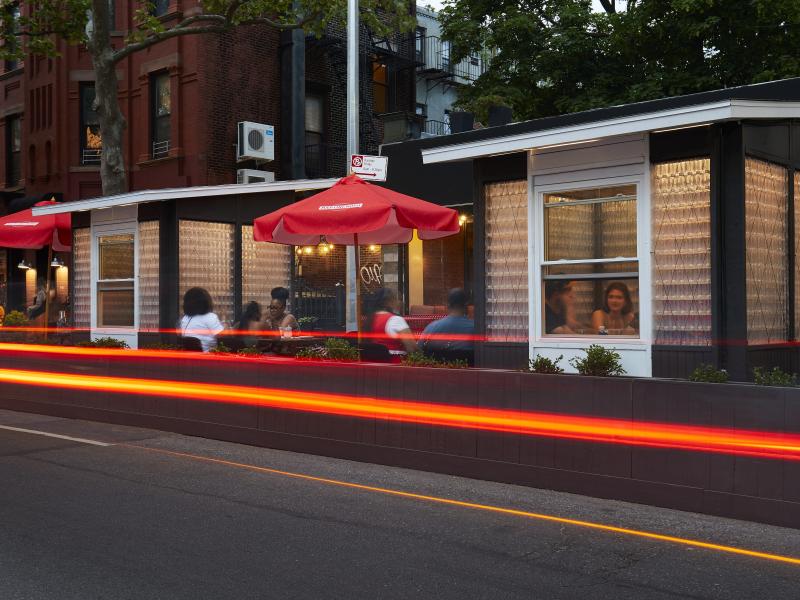 The Future of Smart Outdoor Dining Is Being Built With Upcycled Water Bottles
The Future of Smart Outdoor Dining Is Being Built With Upcycled Water Bottles